In this joint article, FIWARE Community members Robert Brears (Founder, Our Future Water – a FIWARE Foundation media partner), Joris Finck (Product Owner, imec), Salome Leßmann (International Relations and Marketing, it’s OWL Cluster Management), and Ramesh Subryan (Vice President – Global Solutions, NIVID Technologies), showcase how open source tech and open common standards facilitate the development of low-carbon, resource-efficient economies, while avoiding vendor lock-in scenarios.
The traditional global economic model has brought many benefits, and has in many ways improved human wellbeing. At the same time, this model faces increasing challenges from trends such as rapid population growth, urbanisation, inequality and climate change.
Green growth, and cities
In response, many multilateral organisations have called for developing economies that, all in all, result in improved human wellbeing and social equity while significantly reducing environmental risks and ecological scarcities. This means focusing on a transition towards a green economy, to enable economic growth and investment while increasing environmental quality, social inclusiveness and guaranteeing citizens’ privacy.
Cities are facilitating such a transition. They are not only home to the majority of the world’s population and drivers of the global economy, but they are also centres of knowledge and innovation.
Open-source software driving the green economy and green growth in cities
Technological change is a crucial aspect for developing new economies and fostering green growth, which can involve creating new greener technologies and more widespread deployment of existing technologies.
To that end, open-source software promotes collaboration to solve climate change and resource scarcity challenges. For example, open standards allow for the integrating and controlling of a variety of energy and industrial products, enhancing energy efficiency and reducing emissions. Without these standards, a new code would have to be written each time a component needs to talk with another.
Also, open-source software provides a foundation anyone can build on, providing a platform for SMEs, large companies and entrepreneurs to integrate, modify and replicate their green technology products with relatively low adoption costs.
Thanks to the open-source movement, developers, engineers, decision makers and technology end-users can engage with one another on a global scale. The result is a set of dynamic open hardware technologies, faster applications and far more cost-effective services. The practices showcased below are a few examples of how FIWARE is adding to the digital revolution with sustainability in mind.
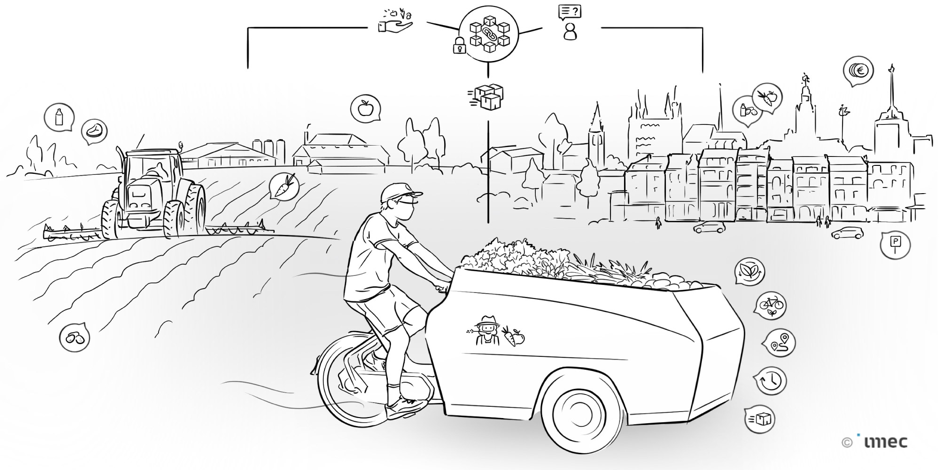
Dynamic access to the city and last mile (food) logistics
The global Covid-19 pandemic is strongly impacting the world’s economy and businesses. However, it is also an opportunity for governments to build recovery plans that can reverse current trends in our consumption and production patterns, towards a more sustainable future.
Despite the strong expectations and awareness of the role of disruptive technologies to transform city operations, there is still uncertainty on how specifically distributed ledger technologies (DLTs) and blockchain can bring significant added value and thoroughly improve the usability and effectiveness of public services, while simultaneously guaranteeing citizens’ privacy.
TOKEN1 is an EU-funded project analysing the impact of DLTs and blockchain technologies in the transformation of public services. Under its umbrella, imec is bringing proven expertise in smart city development and digital technology innovation management. One example of use case is devoted to the promotion of last-mile deliveries and the local economy in the city of Leuven, Belgium.
Local farmers and stores have traditionally faced challenges when distributing and selling their food locally. This process has become even more challenging due to the Covid-19 pandemic. The use-case will contribute to the optimisation of the logistics process, reducing delivery times and costs through a trusted blockchain-based platform, enabling effective logistics tracking and planning, and a distributed interaction with all the actors in the value chain.
The distributed platform is based on an index to grant dynamically calculated preferential access to the city by combining multiple metrics such as sustainability, green mobility, end-to-end routing distance, transport modalities and real-time traffic information. Enabling data sharing while also guaranteeing ownership of the information is distributed among all actors is vital.
The blockchain storage will interact with a dynamic access controller, which will grant extra beneficial rights to logistical players meeting certain conditions (for example, freight consisting of local goods) to enter a certain, restricted area.
The use-case is testing the relevance of dynamic access, starting from local food logistics, and can be expanded to cover other (local) products and new partners. Moreover, the collected information can be applied to support innovative policy making or to improve business processes. Click here to find out more about the TOKEN community.
AI Marketplace: the digital platform for tomorrow’s sustainable innovation
About 85 per cent of manufacturing costs are determined in the product creation process. Hence, driving innovation before products leave the manufacturing floor is key, and artificial intelligence (AI) speaks volumes about how processes can be optimised.
From automating technology scouting to optimising design data to incorporating energy efficiency in the design process, the potential of AI in product creation is manifold. Opinions still diverge widely as to the extent to which AI can reduce a company’s carbon footprint, however – even when managed properly.
As more research is clearly needed on the areas where AI is likely to have an impact on environmental sustainability, another aspect of AI springs to mind. Users such as companies or public administrations often lack sufficient expertise to unlock these potentials. Providers of AI applications, on the other hand, do not have access to domain knowledge to develop solutions for concrete problems currently faced by companies.
An ecosystem for AI in product creation
On that front, the AI Marketplace, a joint initiative driven by several partners from the IT and manufacturing industries, as well as the research community – both FIWARE and it’s OWL Cluster Management are part of the consortium comprised dozens organisations – has been created to narrow the gap between AI providers and users.
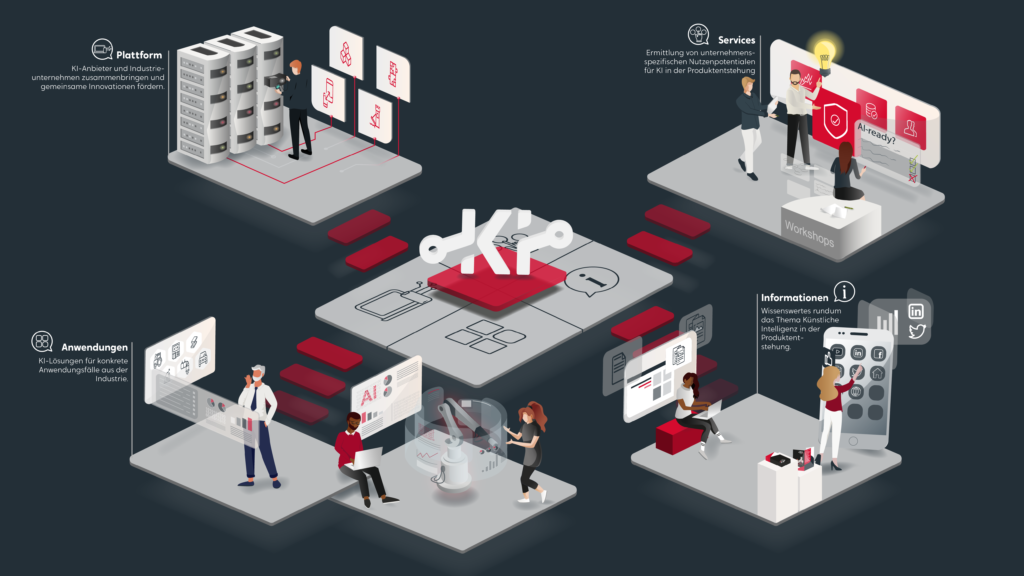
At the forefront of the project is the AI Marketplace platform, where providers, users and experts can develop and exchange AI solutions. The vision is a marketplace that intelligently links platform users – according to their supply and demand profile – while providing a protected space for secure data exchange and data sovereignty.
FIWARE references architecture as a building block
The development of the platform architecture is largely driven by FIWARE. It allows the necessary standards to be set for the AI Marketplace platform and advises on the selection of technologies, reference architectures and standardised APIs.
FIWARE aids in the implementation of the developed concepts and their evaluation and contributes wide expertise in building a marketplace for digital services that deploy FIWARE components and TM Forum APIs.
200 companies and research institutions in the Leading-Edge Cluster it’s OWL are already jointly developing new technologies for the production of tomorrow. The AI Marketplace is heavily contributing to ensuring the competitiveness and sustainability of the industry and significantly increasing the global visibility of Germany in the field of artificial intelligence.
Fully managed IoT platform to create smart, scalable and secure digital solutions
IoT has already secured its place in the digital transformation of cities to deliver innovative and sustainable solutions to solve complex metropolitan challenges of managing water, waste, energy, traffic, parking, ports, healthcare, environment and emergency services, to name but a few.
Even though technology adoption is happening at a rapid pace, disparate data sources, connectivity technologies, high maintenance costs and security risks present daunting challenges for chief information officers (CIOs) and city administrators to fully realise the business value of IoT implementations.
Many organisations embark on developing and deploying their own IoT platform, and often run into unexpected challenges. Urban planning isn’t a straightforward process. Complex research needs to be carried out, many boxes may need to be checked, and countless bureaucracy tends to block the road towards effective problem-solving scenarios.
In short, the process is time-consuming. And as cities worldwide currently face budget constraints, while also having to respond quickly to global pandemics, investing in critical infrastructure such as IoT platforms demands careful considerations and flexible partners.
This drives the need for a robust platform which can process, analyse and use the data and then convert that data into smart city solutions, delivering agile and cost-effective services, positive business outcomes and faster return on investment (ROI).
As a result, Nivid Technologies – a FIWARE Foundation gold member – has joined forces with FIWARE to deliver a high-performing platform aimed at collecting and managing data from the most diverse sources.
Nivid Technologies’ flagship solution, N-Smart, provides a modular, flexible and scalable platform providing a single-pane view for an end-to-end IoT solution. It turns data from a wide variety of sources into useful, contextual information for people to act upon quickly and effectively.
N-Smart comes with operational dashboards and capabilities such as complex event-processing. The platform supports both big data and AI algorithms, while offering different APIs for third-party integration and advanced data-driven maps.
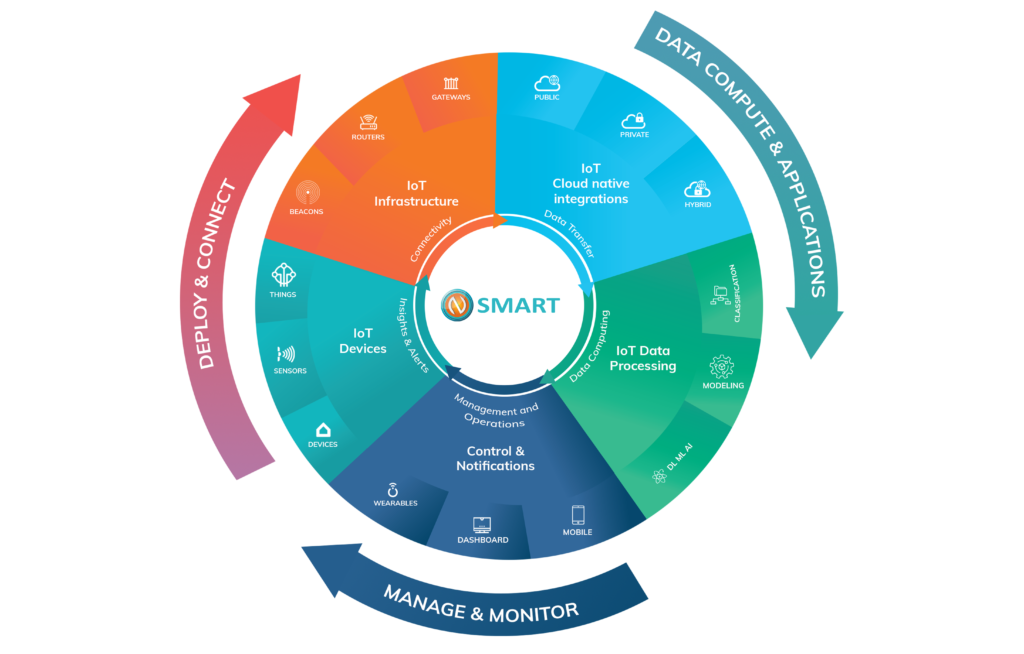
Open standards, transparency and scalability are key for building smart city solutions. FIWARE’s open source platform components breathe reliability and, when combined with N-Smart, result in a wide scope for the development of smart solutions.
Real-time and reliable data offered by the FIWARE platform has helped create applications in a fast and easy manner, not to mention its easy replicability across locations and sectors of the economy.
Nivid’s horizontal solution caters to different business domains including city and government, utilities and infrastructure, healthcare, retail, manufacturing, transportation and logistics, as well as agriculture.
To learn more about the solution, visit www.nsmart.io.
1TOKEN has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under Grant Agreement No. 870603.